3D Scanning Guide


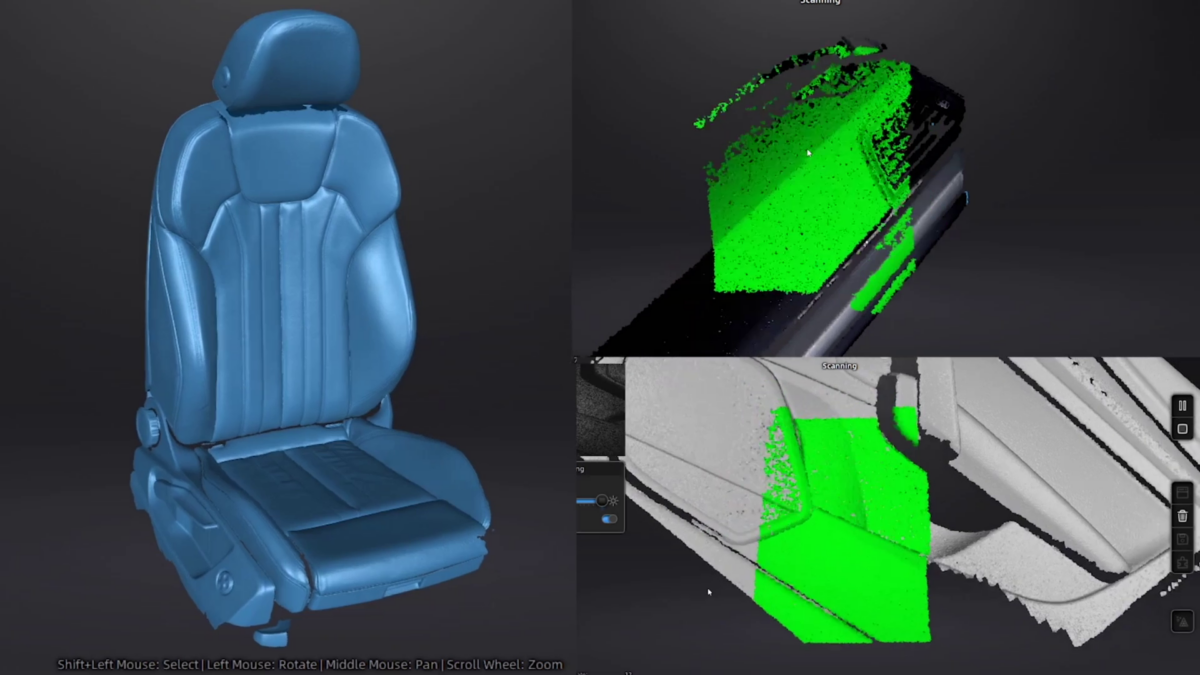
3D scanners are useful tools for professionals in a number of applications, including reverse engineering, ensuring part fit within existing designs, inspections, digitizing historical artifacts, and scanning of faces for dental and orthodontic applications.
In this guide you will learn the 3D scanning process from start to finish using Shining3D’s new handheld EinScan HX 3D scanner.

The EinScan HX Reverse Engineering Design Bundle provides hybrid blue laser and LED light scanning, providing a solution for surfaces that are difficult to scan with traditional white LED technology.

The EinScan H provides hybrid infrared and LED light scanning for scanning hair (normally not possible with previous scanning technology) and a wider range of object size compatibility.
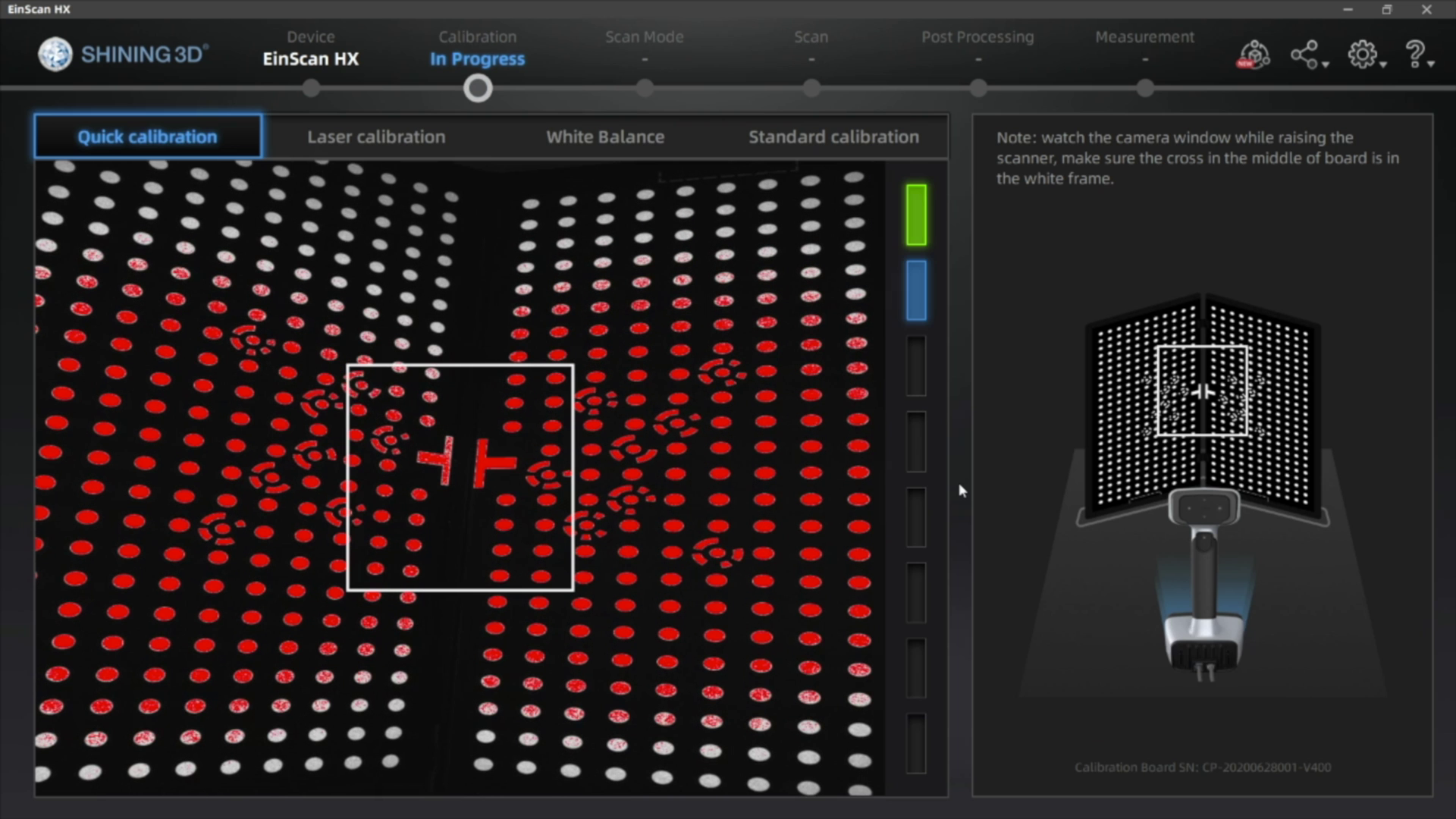
The EinScan scanners require calibration before their first use, as well as after each software update. If calibration is necessary, use your included calibration board and follow the calibration directions as outlined in the software.
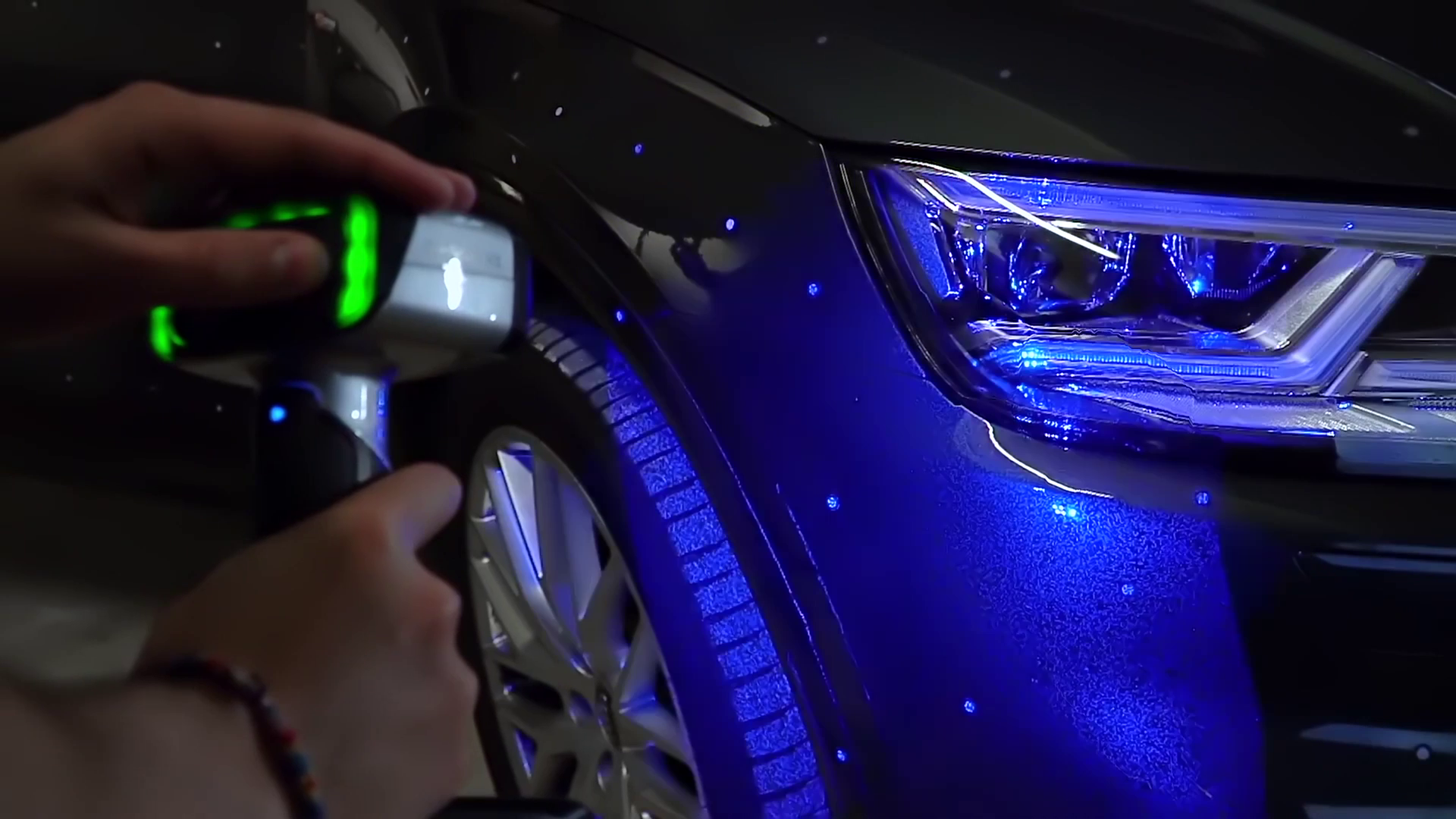
The HX has two scan modes, Rapid Scan and Laser Scan. Rapid scan will need minimal model preparation and will work for most parts, while the laser mode will be best for more accurate results and/or models with darker or shinier surfaces. To begin, we are going to place targets on the model. These targets are used when parts have minimal features or large smooth faces that lack features for the scanner to align itself to. Parts with repetitive features or patterns may confuse the scanner and will require targets placed randomly to help alignment.
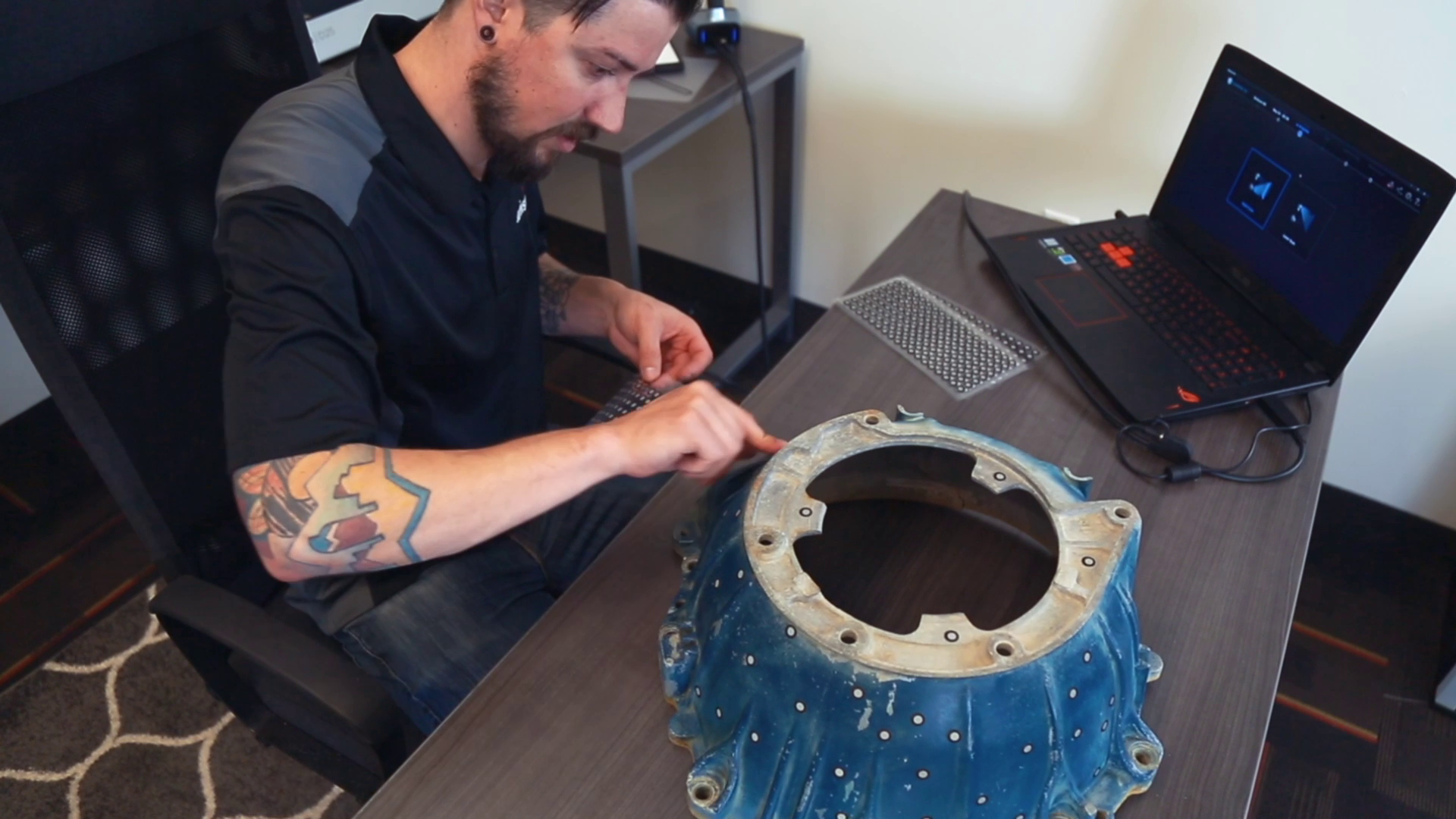
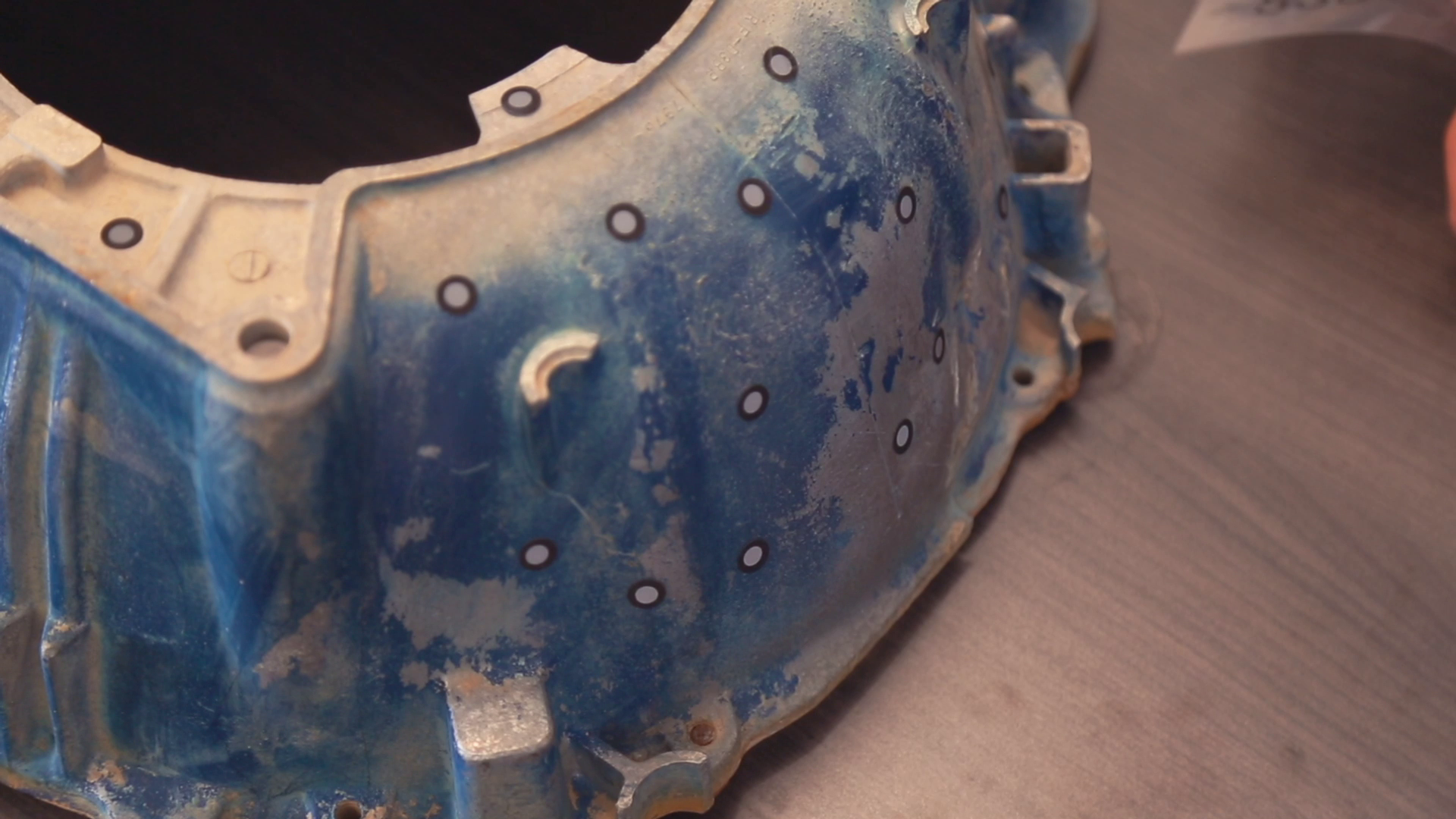


Next, if your model has any shiny, dark, or translucent features you will need to dull them so that they can scan properly. We’re using the HX which is great for shiny and dark materials, and as a result doesn’t really any additional surface treatment.

For best results, avoid very bright rooms or having the scanner directly facing a light source.
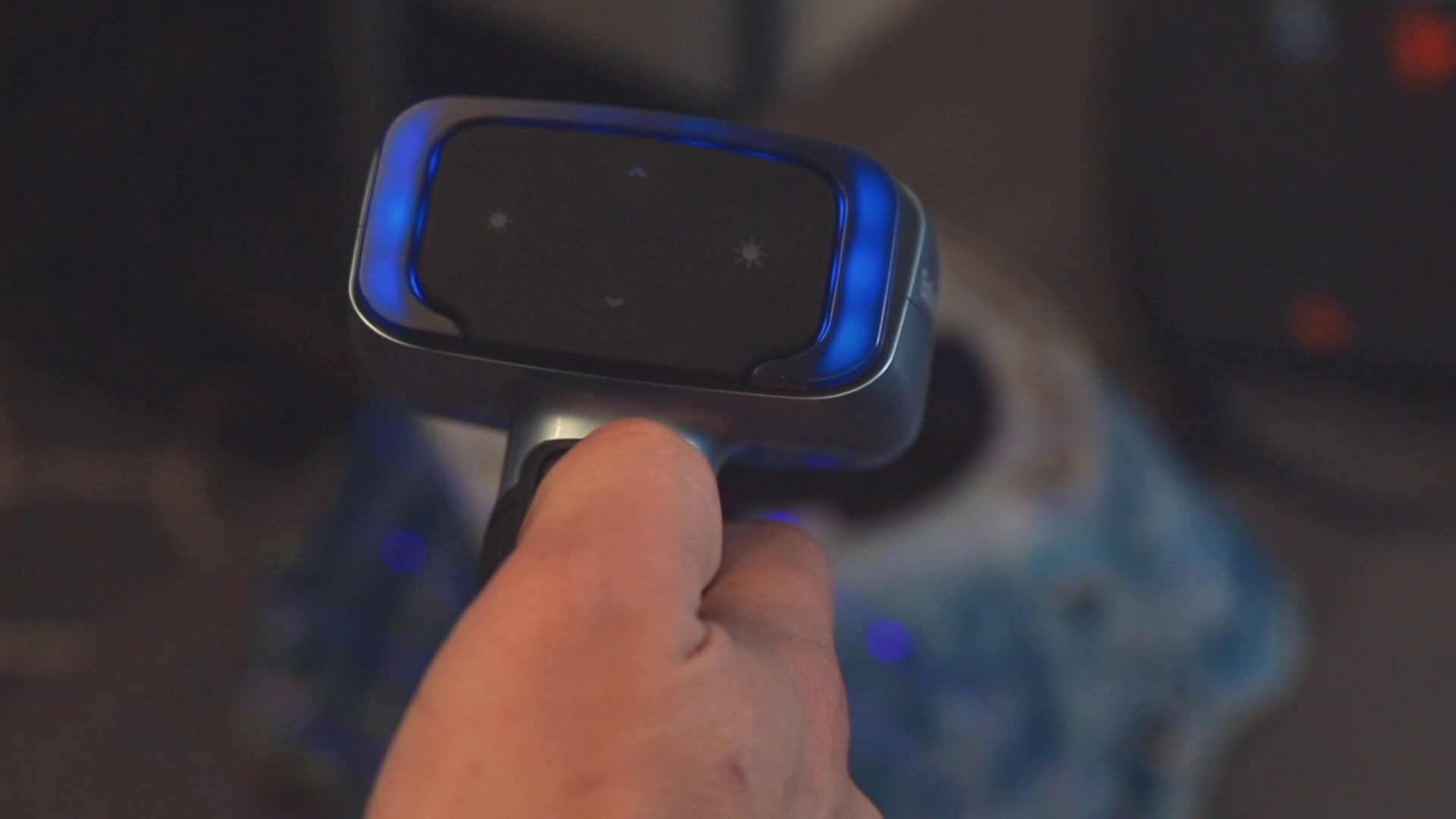

The blue light indicates you’re too far away from the object for proper scanning.
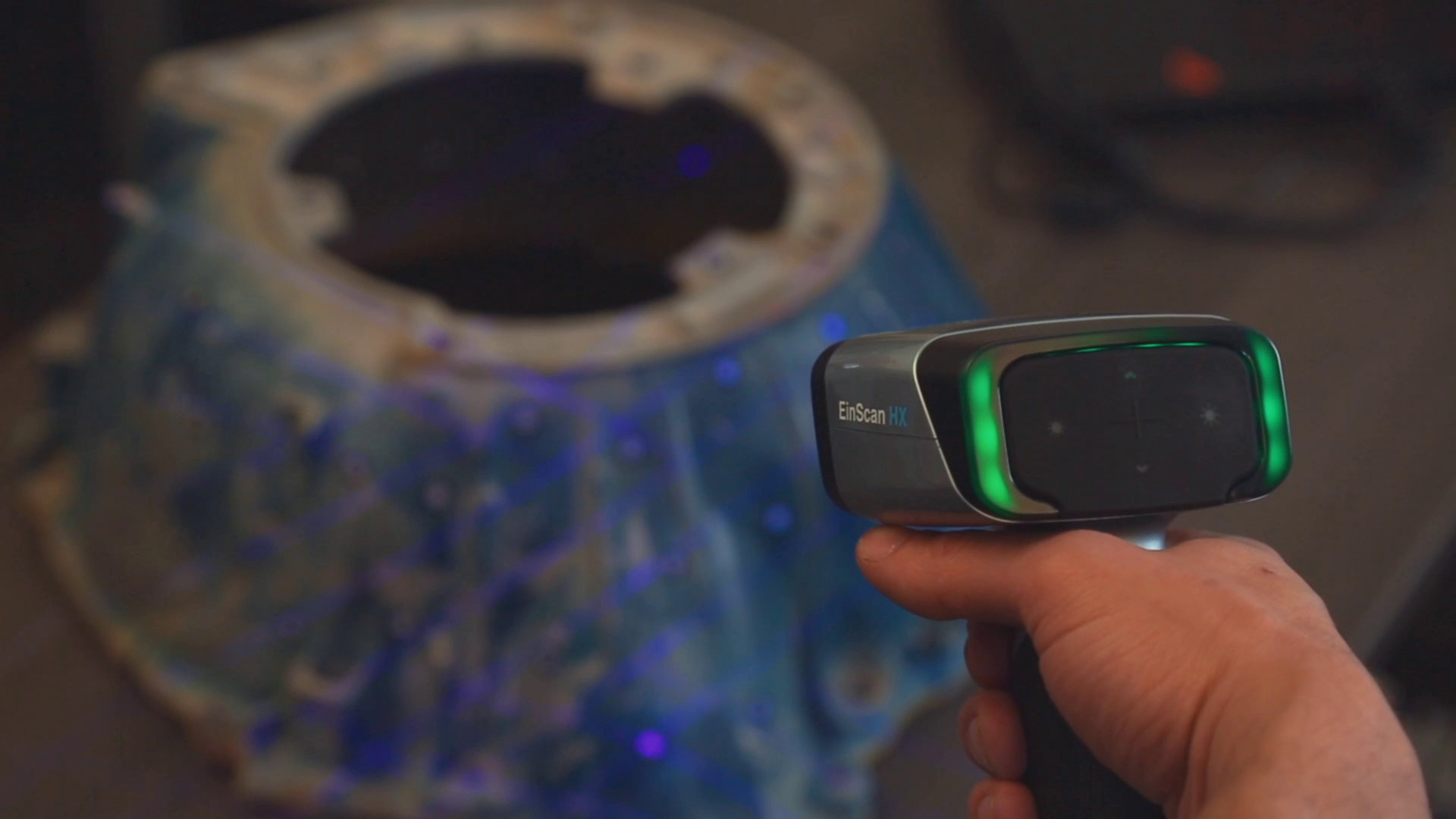

Green is good! You’re right in the sweet spot regarding distance.
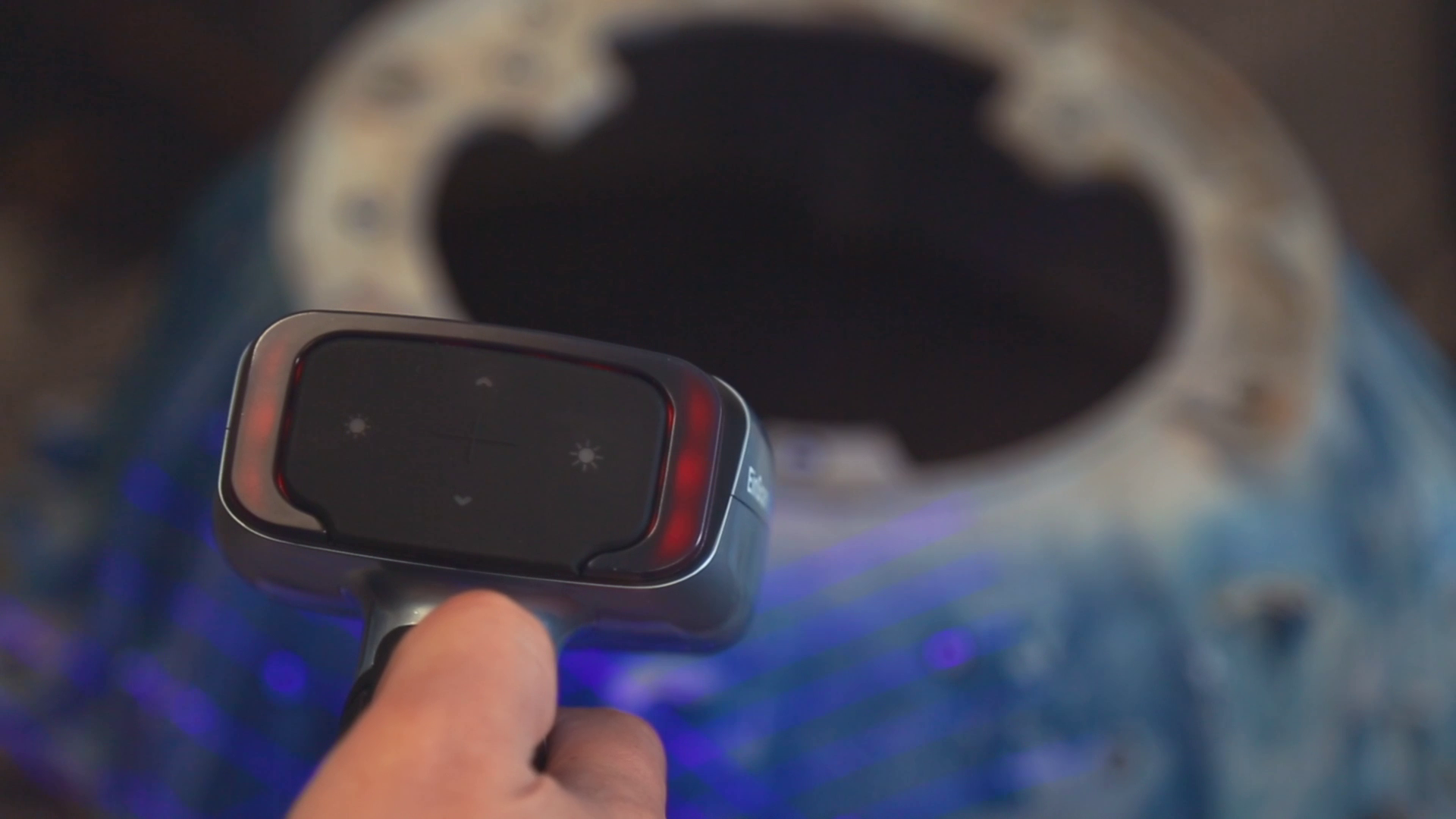

The red light indicates you’re too close to accurately scan the object.
Once you have scanned your object and generated the point cloud data, you can then generate the mesh of your 3D scan. If you’re planning on using scan data for reverse engineering or QC you can export a non-watertight mesh, however for 3D printing you’ll need to make sure you get a watertight model for optimal results.
After you get your mesh data, there are a few different tools that available to help get your 3D model ready to be used.
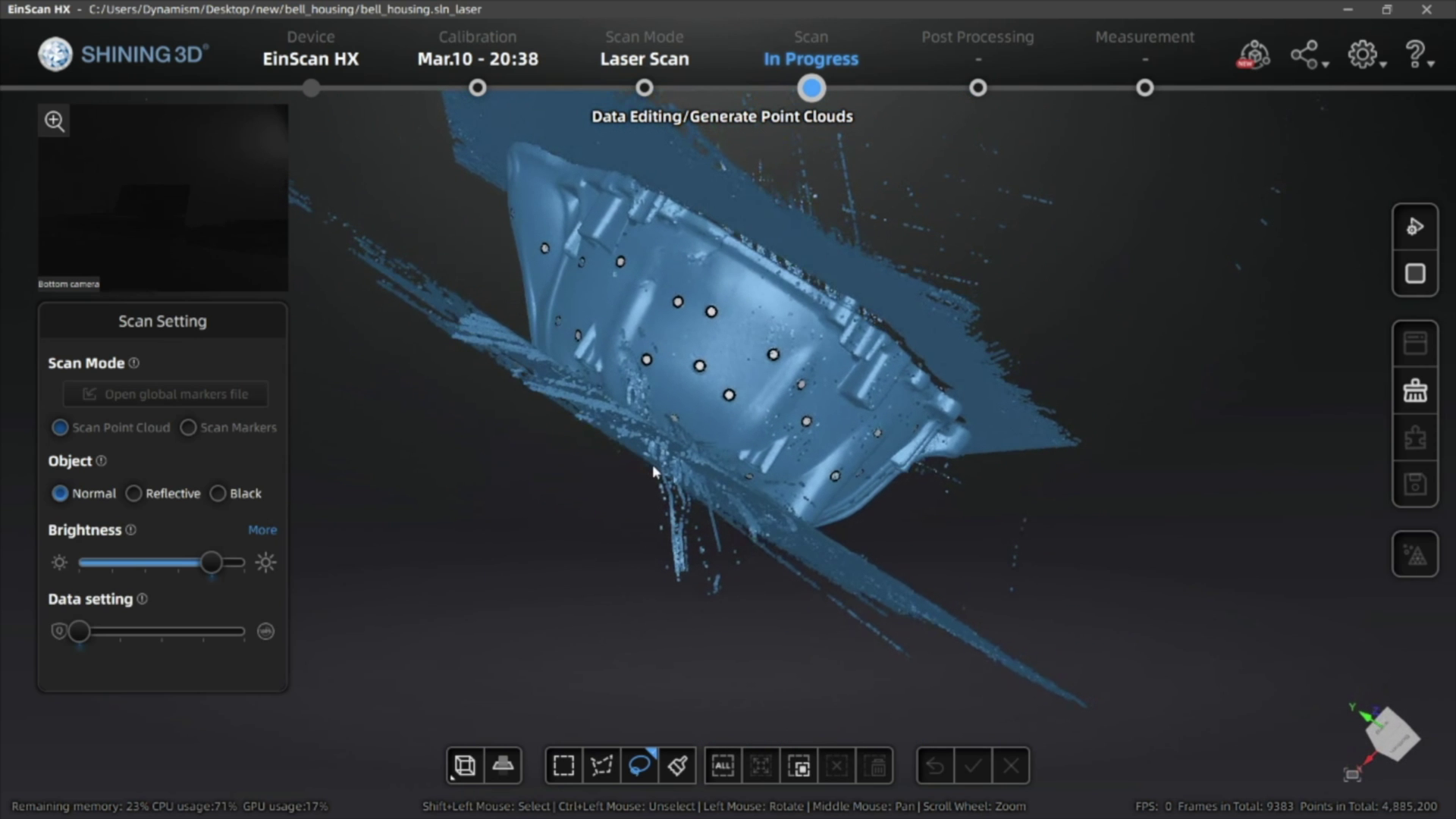
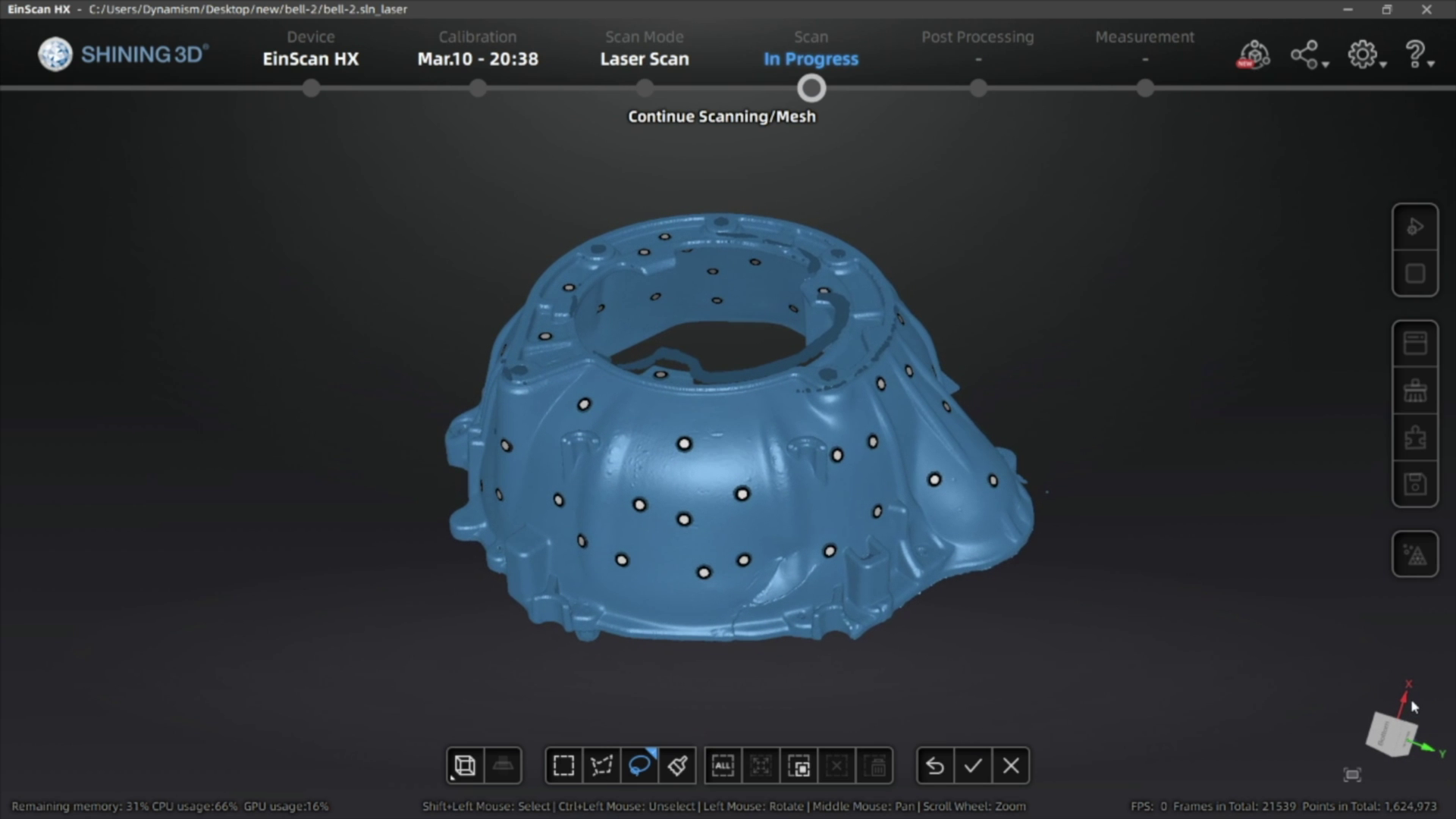
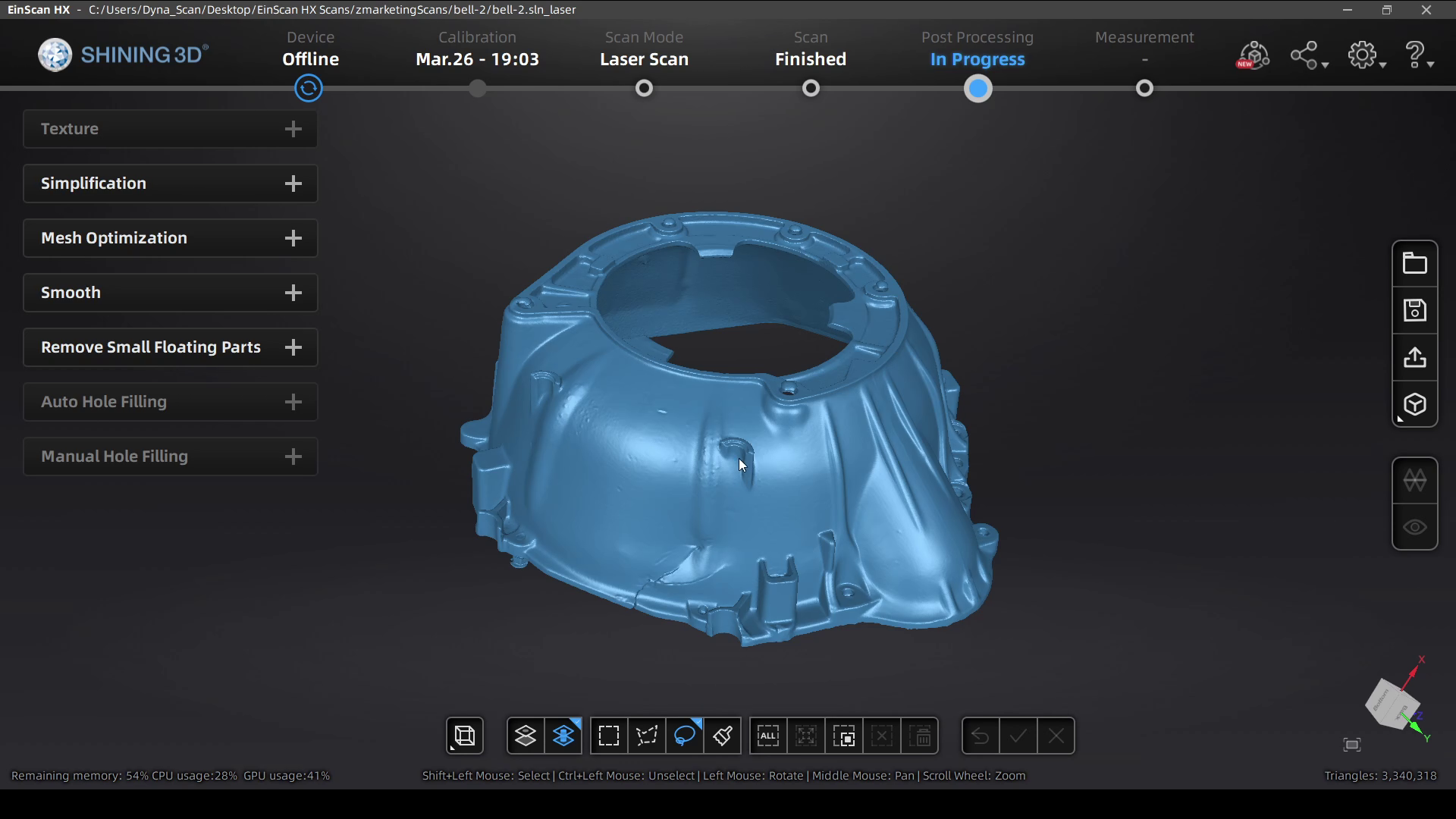
After you’re done with your edits, the mesh files can be exported as an STL, OBJ, 3MF, or PLY file for use in your reverse engineering process, measuring/QC workflow, or to send straight to your slicing software to 3D print!
The HX is the best industrial scanner thanks to it’s specialized blue LED rapid scan mode and high accuracy Laser Scan mode leveraging tracking dots for best accuracy.
The Einscan H uses Infrared technology which is ideal for scanning non-reflective surfaces and capturing details in hard to scan objects like hair.
The Pro HD has a special blue LED light which helps at scanning slightly reflective or darker objects. An additional Color Pack camera can be added for full color scanning.

Whether you’re looking to reverse engineer products, ensure parts fit an assembly, or simply digitizing a part, choosing the right tool for the job is important. In this guidebook we cover all the 3D scanning basics you need to know including: